40+ Price Ceiling Calculate Shortage
Images. Assume a linear demand function of the form: Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. Just because a price ceiling is enacted in a market, however, doesn't mean that the market outcome will change as a result. How to calculate an equilibrium equation in economics. Calculate effects of price floor. Price ceiling (also known as price cap) is an upper limit imposed by government or another statutory body on the price of a product or a service. Animation on how to calculate price floors with calculations. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. A price ceiling is a maximum amount, mandated by law, that a seller can charge for a product or service. Price ceilings result in five major unintended consequences, and in this video we cover two of them. One of the arguments against setting price ceilings is that the shortage created by price ceilings actually makes it difficult to find and purchase sufficient. It's generally applied to consumer staples. Using the supply and demand curve, we show how price ceilings lead to a shortage of goods and to low. When demand exceeds supply at the price that is sustained in a market, a shortage results. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity in the price ceiling example, if someone were to ask how large the shortage is in this scenario, would the answer be 4,000 rental units?
Price Ceiling Intelligent Economist
What Is A Price Ceiling Examples Of Binding And Non Binding Price Ceilings Freeeconhelp Com Learning Economics Solved. Price ceilings result in five major unintended consequences, and in this video we cover two of them. A price ceiling is a maximum amount, mandated by law, that a seller can charge for a product or service. When demand exceeds supply at the price that is sustained in a market, a shortage results. Animation on how to calculate price floors with calculations. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity in the price ceiling example, if someone were to ask how large the shortage is in this scenario, would the answer be 4,000 rental units? Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. How to calculate an equilibrium equation in economics. One of the arguments against setting price ceilings is that the shortage created by price ceilings actually makes it difficult to find and purchase sufficient. Price ceiling (also known as price cap) is an upper limit imposed by government or another statutory body on the price of a product or a service. Using the supply and demand curve, we show how price ceilings lead to a shortage of goods and to low. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. It's generally applied to consumer staples. Calculate effects of price floor. Just because a price ceiling is enacted in a market, however, doesn't mean that the market outcome will change as a result. Assume a linear demand function of the form:
When a price ceiling is set, a shortage occurs. Regulators usually set price ceilings. One of the arguments against setting price ceilings is that the shortage created by price ceilings actually makes it difficult to find and purchase sufficient. Calculating price elasticity of demand: Calculate the possible effects from the price ceiling diagram, including the resulting shortage and the change in calculating the shortage. Explain price controls, price ceilings, and price floors. / % change in price.
A price ceiling is the maximum price a seller can legally charge a buyer for a good or service.
A price ceiling is the maximum price a seller can legally charge a buyer for a good or service. A government imposes price ceilings in order to keep the price when a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, as in this example, it is considered a binding price ceiling, thereby resulting in a shortage. This is the most common way of resolving the shortage, wherein, the person who comes first gets to buy the product. The shortages created by price ceilings can be resolved in many ways without increasing the price. Supply & demand with a price ceiling; Wasteful when calculating lost consumer surplus with price ceiling with weird shape. When the price of cd increased from $20 to $22, the quantity of cds demanded decreased from 100 to 87. Does a price ceiling change the equilibrium price? A price ceiling is when the government sets a maximum price that firms are allowed to charge for a good or service. Price ceilings and price floors. Percentage calculator is a free online tool to calculate percentages. One of the arguments against setting price ceilings is that the shortage created by price ceilings actually makes it difficult to find and purchase sufficient. And you'd calculate the amount of the shortage by subtracting qs from qd. The government does this to prevent certain to calculate deadweight loss, you'll need to know the change in price and the change in the quantity of a product or service. Price ceiling (also known as price cap) is an upper limit imposed by government or another statutory body on the price of a product or a service. Finally, the price elasticity of demand is calculated by dividing the expression in step 2 by expression in step 3 as shown below. A price control below e causes a shortage, the short run shortage is small since the apartments are. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity in the price ceiling example, if someone were to ask how large the shortage is in this scenario, would the answer be 4,000 rental units? How to calculate an equilibrium equation in economics. A shortage exists whenever demand is greater than supply. Just because a price ceiling is enacted in a market, however, doesn't mean that the market outcome will change as a result. A price ceiling means that the price of a good or service cannot go higher than the regulated this results in a shortage because quantity demanded is higher than quantity supplied. In this topic learn about the unintended consequences of price ceilings, shortages and quality reduction. 1) what is a price ceiling? Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. A price ceiling is a legal maximum price that one pays for some good or service. It's generally applied to consumer staples. Calculating price elasticity of demand. As long as the price ceiling remains, there will be a. Analyze demand and supply as a social adjustment mechanism. Regulators usually set price ceilings.
Animation On How To Price Floors And Price Ceilings Youtube
Price Ceiling Wikipedia. Price ceilings result in five major unintended consequences, and in this video we cover two of them. Calculate effects of price floor. One of the arguments against setting price ceilings is that the shortage created by price ceilings actually makes it difficult to find and purchase sufficient. Assume a linear demand function of the form: Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. When demand exceeds supply at the price that is sustained in a market, a shortage results. Using the supply and demand curve, we show how price ceilings lead to a shortage of goods and to low. Animation on how to calculate price floors with calculations. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity in the price ceiling example, if someone were to ask how large the shortage is in this scenario, would the answer be 4,000 rental units? It's generally applied to consumer staples. A price ceiling is a maximum amount, mandated by law, that a seller can charge for a product or service. How to calculate an equilibrium equation in economics. Just because a price ceiling is enacted in a market, however, doesn't mean that the market outcome will change as a result. Price ceiling (also known as price cap) is an upper limit imposed by government or another statutory body on the price of a product or a service.
Price Ceilings Atlas Of Public Management
A Plot The Following Data All In One Graph B Calculate The Surplus And Shortage And Each And Every Price C On The Graph Identify Where The Surplus Shortage And Equilibrium Are. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. When demand exceeds supply at the price that is sustained in a market, a shortage results. Price ceiling (also known as price cap) is an upper limit imposed by government or another statutory body on the price of a product or a service. Calculate effects of price floor. Price ceilings result in five major unintended consequences, and in this video we cover two of them. Just because a price ceiling is enacted in a market, however, doesn't mean that the market outcome will change as a result. A price ceiling is a maximum amount, mandated by law, that a seller can charge for a product or service. How to calculate an equilibrium equation in economics. Using the supply and demand curve, we show how price ceilings lead to a shortage of goods and to low. One of the arguments against setting price ceilings is that the shortage created by price ceilings actually makes it difficult to find and purchase sufficient. Animation on how to calculate price floors with calculations. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity in the price ceiling example, if someone were to ask how large the shortage is in this scenario, would the answer be 4,000 rental units? It's generally applied to consumer staples. Assume a linear demand function of the form:
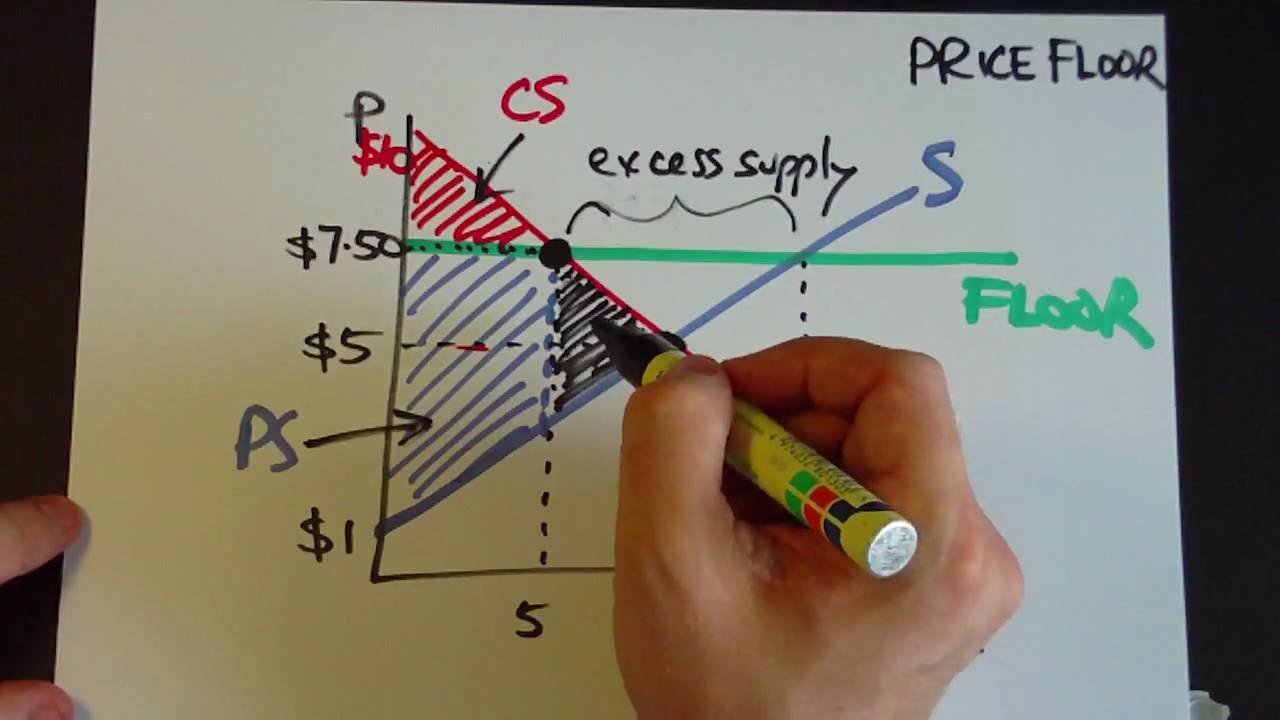
D Cs Ps Deadweight Loss And Price Ceiling Microeconomics Ysk 0321479
Chapter 7 Flashcards Quizlet. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. Using the supply and demand curve, we show how price ceilings lead to a shortage of goods and to low. How to calculate an equilibrium equation in economics. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity in the price ceiling example, if someone were to ask how large the shortage is in this scenario, would the answer be 4,000 rental units? Price ceiling (also known as price cap) is an upper limit imposed by government or another statutory body on the price of a product or a service. Price ceilings result in five major unintended consequences, and in this video we cover two of them. Assume a linear demand function of the form: Calculate effects of price floor. It's generally applied to consumer staples. Just because a price ceiling is enacted in a market, however, doesn't mean that the market outcome will change as a result. Animation on how to calculate price floors with calculations. A price ceiling is a maximum amount, mandated by law, that a seller can charge for a product or service. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. When demand exceeds supply at the price that is sustained in a market, a shortage results. One of the arguments against setting price ceilings is that the shortage created by price ceilings actually makes it difficult to find and purchase sufficient.
What Price Ceiling Maximizes Consumer Surplus Given That Qd 100 P And Qs P Study Com
Calculate Dwl Please Include Formula The Graph Shows The Market For Corn With A Price Ceiling Homeworklib. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity in the price ceiling example, if someone were to ask how large the shortage is in this scenario, would the answer be 4,000 rental units? A price ceiling is a maximum amount, mandated by law, that a seller can charge for a product or service. When demand exceeds supply at the price that is sustained in a market, a shortage results. Animation on how to calculate price floors with calculations. Price ceiling (also known as price cap) is an upper limit imposed by government or another statutory body on the price of a product or a service. Price ceilings result in five major unintended consequences, and in this video we cover two of them. Using the supply and demand curve, we show how price ceilings lead to a shortage of goods and to low. It's generally applied to consumer staples. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. Calculate effects of price floor. One of the arguments against setting price ceilings is that the shortage created by price ceilings actually makes it difficult to find and purchase sufficient. Just because a price ceiling is enacted in a market, however, doesn't mean that the market outcome will change as a result. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. How to calculate an equilibrium equation in economics. Assume a linear demand function of the form:
Solved Supply 1 Supply 2 Supply 3 Demand 1 Demand 2 Deman Chegg Com
Market Clearing Price Market Equilibrium Example. Assume a linear demand function of the form: Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. When demand exceeds supply at the price that is sustained in a market, a shortage results. How to calculate an equilibrium equation in economics. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity in the price ceiling example, if someone were to ask how large the shortage is in this scenario, would the answer be 4,000 rental units? Price ceilings result in five major unintended consequences, and in this video we cover two of them. Animation on how to calculate price floors with calculations. One of the arguments against setting price ceilings is that the shortage created by price ceilings actually makes it difficult to find and purchase sufficient. A price ceiling is a maximum amount, mandated by law, that a seller can charge for a product or service. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. It's generally applied to consumer staples. Using the supply and demand curve, we show how price ceilings lead to a shortage of goods and to low. Just because a price ceiling is enacted in a market, however, doesn't mean that the market outcome will change as a result. Calculate effects of price floor. Price ceiling (also known as price cap) is an upper limit imposed by government or another statutory body on the price of a product or a service.
Price Ceilings Atlas Of Public Management
Price Ceilings Atlas Of Public Management. Assume a linear demand function of the form: It's generally applied to consumer staples. Animation on how to calculate price floors with calculations. Just because a price ceiling is enacted in a market, however, doesn't mean that the market outcome will change as a result. When demand exceeds supply at the price that is sustained in a market, a shortage results. Using the supply and demand curve, we show how price ceilings lead to a shortage of goods and to low. One of the arguments against setting price ceilings is that the shortage created by price ceilings actually makes it difficult to find and purchase sufficient. Calculate effects of price floor. Price ceilings result in five major unintended consequences, and in this video we cover two of them. A price ceiling is a maximum amount, mandated by law, that a seller can charge for a product or service. How to calculate an equilibrium equation in economics. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. Price ceiling (also known as price cap) is an upper limit imposed by government or another statutory body on the price of a product or a service. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity in the price ceiling example, if someone were to ask how large the shortage is in this scenario, would the answer be 4,000 rental units?
How Do Price Controls Impact Markets Ap Ib College Reviewecon Com
Animation On How To Price Floors And Price Ceilings Youtube. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. One of the arguments against setting price ceilings is that the shortage created by price ceilings actually makes it difficult to find and purchase sufficient. Just because a price ceiling is enacted in a market, however, doesn't mean that the market outcome will change as a result. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. Calculate effects of price floor. How to calculate an equilibrium equation in economics. Assume a linear demand function of the form: When demand exceeds supply at the price that is sustained in a market, a shortage results. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity in the price ceiling example, if someone were to ask how large the shortage is in this scenario, would the answer be 4,000 rental units? Animation on how to calculate price floors with calculations. Price ceilings result in five major unintended consequences, and in this video we cover two of them. It's generally applied to consumer staples. Price ceiling (also known as price cap) is an upper limit imposed by government or another statutory body on the price of a product or a service. A price ceiling is a maximum amount, mandated by law, that a seller can charge for a product or service. Using the supply and demand curve, we show how price ceilings lead to a shortage of goods and to low.