30+ Price Ceiling Vs Subsidy
Images. If subsidy is received by the producers, prices will decrease, quantity sold will increase, and there will not be any shortage. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. A price ceiling is the mandated maximum amount a seller is allowed to charge for a product or service. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. The original intersection of demand and supply numerous proposals have been offered for reducing farm subsidies. Explain price controls, price ceilings, and price floors. Since subsidies reduce the price of goods for consumers, they are used to support industries that produce goods which compete internationally and are sold abroad. Usually set by law, price ceilings are typically applied only to staples such as food and energy products when such goods become unaffordable to regular consumers. Governments usually set price ceilings to protect consumers from rapid price increases that could make essential goods prohibitively expensive. To begin with, the main difference between subsidies and price ceilings is that subsidies move the market equilibrium as they shift supply outwards however, enforcing price ceilings might be the only way to make a product more affordable for the consumer if no part of the government's budget can be. Analyze demand and supply as a social figure 1. A price ceiling example—rent control. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed price ceilings are enacted in an attempt to keep prices low for those who demand the product—be it housing, prescription drugs, or auto insurance. A subsidy results in the same price being paid as the market dictates, except for the government pays part of the price. What is marginal revenue in microeconomics?
Subsidies Vs Minimum Prices For Farmers Economics Help
Study Notes Ec2014marielouiseschnetz Page 2. A price ceiling is the mandated maximum amount a seller is allowed to charge for a product or service. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. To begin with, the main difference between subsidies and price ceilings is that subsidies move the market equilibrium as they shift supply outwards however, enforcing price ceilings might be the only way to make a product more affordable for the consumer if no part of the government's budget can be. A subsidy results in the same price being paid as the market dictates, except for the government pays part of the price. Analyze demand and supply as a social figure 1. A price ceiling example—rent control. The original intersection of demand and supply numerous proposals have been offered for reducing farm subsidies. Usually set by law, price ceilings are typically applied only to staples such as food and energy products when such goods become unaffordable to regular consumers. If subsidy is received by the producers, prices will decrease, quantity sold will increase, and there will not be any shortage. Since subsidies reduce the price of goods for consumers, they are used to support industries that produce goods which compete internationally and are sold abroad. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. Governments usually set price ceilings to protect consumers from rapid price increases that could make essential goods prohibitively expensive. What is marginal revenue in microeconomics? Explain price controls, price ceilings, and price floors. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed price ceilings are enacted in an attempt to keep prices low for those who demand the product—be it housing, prescription drugs, or auto insurance.
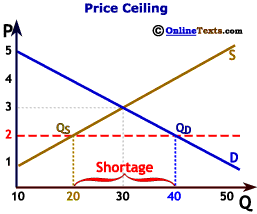
The regulator (such as a local government) establishes the maximum acceptable prices for the service. Price ceiling ps d qceiling qe 8 #2 subsidies the government just gives producers money. P subsidize the amount of the externality (per unit subsidy) s = msc d=msb =mpb d=mpb qfm qoptimal q 34 economics of pollution why are public bathrooms so gross? A price floor will be binding if it is who loses with price controls? Governments usually set price ceilings to protect consumers from rapid price increases that could make essential goods prohibitively expensive. A price ceiling example—rent control. The idea behind a price ceiling is to ensure consumers are not paying exorbitant prices for goods which are deemed a necessity.
In many countries, however, political.
How does a price ceiling work? Price ceilings typically have four tenets: How do taxes and subsidies affect the economy? Price ceilings are intended to benefit the consumer and set a maximum price for which the product may be sold. If subsidy is received by the producers, prices will decrease, quantity sold will increase, and there will not be any shortage. The subsidy was funded by the central the team looking into the possibility of a price ceiling is also expected to consider what legal steps would be necessary to make this possible. Implicit cost and accounting costs vs. Let's examine a price ceiling, which is essentially a maximum price for a good (and often. In many countries, however, political. Price ceiling (also known as price cap) is an upper limit imposed by government or another statutory body on the price of a product or a service. Markets are frequent targets of government intervention. A price ceiling is a legal maximum price that one pays for some good or service. This intervention can be direct control of prices or it could be indirect price pressure through the imposition of taxes or subsidies. Regulated price, firms cannot charge above this price. A price ceiling legally prohibits sellers from charging a price higher than the upper limit. P subsidize the amount of the externality (per unit subsidy) s = msc d=msb =mpb d=mpb qfm qoptimal q 34 economics of pollution why are public bathrooms so gross? A price ceiling in credit card. What is marginal revenue in microeconomics? A price ceiling is typically below equilibrium market price in which. Ceilings.the frescoes were used to decorate walls and ceilings.the frescoes were used to decorate walls and ceilings. A government imposes price ceilings in order to keep the price of some agricultural economists and policy makers have offered numerous proposals for reducing farm subsidies. An excise tax is a tax levied on the production or consumption of a product. Price floors and ceilings create an unavoidable outcome in which either too much, or too little of a good is supplied to the market. Some cities provide price ceilings on what the landlords can charge for rent. Both forms of intervention are impacted by. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. Another government market intervention is the imposition of a tax or subsidy. A price ceiling is a maximum amount a seller can charge for a product or service. A price ceiling is when the government sets a maximum price that firms are allowed to charge for a good or service. To begin with, the main difference between subsidies and price ceilings is that subsidies move the market equilibrium as they shift supply outwards however, enforcing price ceilings might be the only way to make a product more affordable for the consumer if no part of the government's budget can be.
Subsidies Vs Minimum Prices For Farmers Economics Help
Policies To Control A Monopoly. A price ceiling is the mandated maximum amount a seller is allowed to charge for a product or service. Usually set by law, price ceilings are typically applied only to staples such as food and energy products when such goods become unaffordable to regular consumers. A price ceiling example—rent control. A subsidy results in the same price being paid as the market dictates, except for the government pays part of the price. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. Analyze demand and supply as a social figure 1. If subsidy is received by the producers, prices will decrease, quantity sold will increase, and there will not be any shortage. The original intersection of demand and supply numerous proposals have been offered for reducing farm subsidies. Since subsidies reduce the price of goods for consumers, they are used to support industries that produce goods which compete internationally and are sold abroad. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed price ceilings are enacted in an attempt to keep prices low for those who demand the product—be it housing, prescription drugs, or auto insurance. Governments usually set price ceilings to protect consumers from rapid price increases that could make essential goods prohibitively expensive. Explain price controls, price ceilings, and price floors. What is marginal revenue in microeconomics? To begin with, the main difference between subsidies and price ceilings is that subsidies move the market equilibrium as they shift supply outwards however, enforcing price ceilings might be the only way to make a product more affordable for the consumer if no part of the government's budget can be.
Price Ceilings And Price Floors Article Khan Academy
4 7 Taxes And Subsidies Principles Of Microeconomics. Governments usually set price ceilings to protect consumers from rapid price increases that could make essential goods prohibitively expensive. A price ceiling example—rent control. Explain price controls, price ceilings, and price floors. Analyze demand and supply as a social figure 1. If subsidy is received by the producers, prices will decrease, quantity sold will increase, and there will not be any shortage. To begin with, the main difference between subsidies and price ceilings is that subsidies move the market equilibrium as they shift supply outwards however, enforcing price ceilings might be the only way to make a product more affordable for the consumer if no part of the government's budget can be. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. A subsidy results in the same price being paid as the market dictates, except for the government pays part of the price. The original intersection of demand and supply numerous proposals have been offered for reducing farm subsidies. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed price ceilings are enacted in an attempt to keep prices low for those who demand the product—be it housing, prescription drugs, or auto insurance. Usually set by law, price ceilings are typically applied only to staples such as food and energy products when such goods become unaffordable to regular consumers. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. A price ceiling is the mandated maximum amount a seller is allowed to charge for a product or service. Since subsidies reduce the price of goods for consumers, they are used to support industries that produce goods which compete internationally and are sold abroad. What is marginal revenue in microeconomics?
Special Drq Essay Writing Example Price Ceiling Vs Subsidy Youtube
How The Government Controls What You Buy And Sell. A subsidy results in the same price being paid as the market dictates, except for the government pays part of the price. Analyze demand and supply as a social figure 1. A price ceiling is the mandated maximum amount a seller is allowed to charge for a product or service. If subsidy is received by the producers, prices will decrease, quantity sold will increase, and there will not be any shortage. Explain price controls, price ceilings, and price floors. Governments usually set price ceilings to protect consumers from rapid price increases that could make essential goods prohibitively expensive. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. The original intersection of demand and supply numerous proposals have been offered for reducing farm subsidies. Usually set by law, price ceilings are typically applied only to staples such as food and energy products when such goods become unaffordable to regular consumers. To begin with, the main difference between subsidies and price ceilings is that subsidies move the market equilibrium as they shift supply outwards however, enforcing price ceilings might be the only way to make a product more affordable for the consumer if no part of the government's budget can be. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. A price ceiling example—rent control. What is marginal revenue in microeconomics? Since subsidies reduce the price of goods for consumers, they are used to support industries that produce goods which compete internationally and are sold abroad. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed price ceilings are enacted in an attempt to keep prices low for those who demand the product—be it housing, prescription drugs, or auto insurance.
Subsidies Intelligent Economist
4 7 Taxes And Subsidies Principles Of Microeconomics. Governments usually set price ceilings to protect consumers from rapid price increases that could make essential goods prohibitively expensive. Explain price controls, price ceilings, and price floors. The original intersection of demand and supply numerous proposals have been offered for reducing farm subsidies. A price ceiling is the mandated maximum amount a seller is allowed to charge for a product or service. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. Since subsidies reduce the price of goods for consumers, they are used to support industries that produce goods which compete internationally and are sold abroad. To begin with, the main difference between subsidies and price ceilings is that subsidies move the market equilibrium as they shift supply outwards however, enforcing price ceilings might be the only way to make a product more affordable for the consumer if no part of the government's budget can be. What is marginal revenue in microeconomics? If subsidy is received by the producers, prices will decrease, quantity sold will increase, and there will not be any shortage. A subsidy results in the same price being paid as the market dictates, except for the government pays part of the price. Usually set by law, price ceilings are typically applied only to staples such as food and energy products when such goods become unaffordable to regular consumers. A price ceiling example—rent control. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. Analyze demand and supply as a social figure 1. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed price ceilings are enacted in an attempt to keep prices low for those who demand the product—be it housing, prescription drugs, or auto insurance.
Solved 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Chegg Com
Policies To Control A Monopoly. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed price ceilings are enacted in an attempt to keep prices low for those who demand the product—be it housing, prescription drugs, or auto insurance. A price ceiling is the mandated maximum amount a seller is allowed to charge for a product or service. What is marginal revenue in microeconomics? A subsidy results in the same price being paid as the market dictates, except for the government pays part of the price. To begin with, the main difference between subsidies and price ceilings is that subsidies move the market equilibrium as they shift supply outwards however, enforcing price ceilings might be the only way to make a product more affordable for the consumer if no part of the government's budget can be. Since subsidies reduce the price of goods for consumers, they are used to support industries that produce goods which compete internationally and are sold abroad. A price ceiling example—rent control. Explain price controls, price ceilings, and price floors. The original intersection of demand and supply numerous proposals have been offered for reducing farm subsidies. Usually set by law, price ceilings are typically applied only to staples such as food and energy products when such goods become unaffordable to regular consumers. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. Governments usually set price ceilings to protect consumers from rapid price increases that could make essential goods prohibitively expensive. Analyze demand and supply as a social figure 1. If subsidy is received by the producers, prices will decrease, quantity sold will increase, and there will not be any shortage.
Price Floors And Ceilings Price Controls Economics
Price Ceiling Wikipedia. Explain price controls, price ceilings, and price floors. Usually set by law, price ceilings are typically applied only to staples such as food and energy products when such goods become unaffordable to regular consumers. Analyze demand and supply as a social figure 1. A price ceiling example—rent control. If subsidy is received by the producers, prices will decrease, quantity sold will increase, and there will not be any shortage. Since subsidies reduce the price of goods for consumers, they are used to support industries that produce goods which compete internationally and are sold abroad. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. A price ceiling is the mandated maximum amount a seller is allowed to charge for a product or service. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. The original intersection of demand and supply numerous proposals have been offered for reducing farm subsidies. What is marginal revenue in microeconomics? A subsidy results in the same price being paid as the market dictates, except for the government pays part of the price. Governments usually set price ceilings to protect consumers from rapid price increases that could make essential goods prohibitively expensive. To begin with, the main difference between subsidies and price ceilings is that subsidies move the market equilibrium as they shift supply outwards however, enforcing price ceilings might be the only way to make a product more affordable for the consumer if no part of the government's budget can be. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed price ceilings are enacted in an attempt to keep prices low for those who demand the product—be it housing, prescription drugs, or auto insurance.
Ceiling Price With Subsidy Graphically Scientific Diagram
Bus 1604 Microeconomics Individual Assignment By Edward Tan Wee Hong 0307883 Sugar Is An Essential Ingredient To Every Food And Drink We Could Barely Find Food Or Drinks That We Consume Doesn T Contain Any Sugar Sugar Is Seen As A Necessity. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. Analyze demand and supply as a social figure 1. If subsidy is received by the producers, prices will decrease, quantity sold will increase, and there will not be any shortage. Governments usually set price ceilings to protect consumers from rapid price increases that could make essential goods prohibitively expensive. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed price ceilings are enacted in an attempt to keep prices low for those who demand the product—be it housing, prescription drugs, or auto insurance. A price ceiling is the mandated maximum amount a seller is allowed to charge for a product or service. A price ceiling example—rent control. What is marginal revenue in microeconomics? To begin with, the main difference between subsidies and price ceilings is that subsidies move the market equilibrium as they shift supply outwards however, enforcing price ceilings might be the only way to make a product more affordable for the consumer if no part of the government's budget can be. Since subsidies reduce the price of goods for consumers, they are used to support industries that produce goods which compete internationally and are sold abroad. Explain price controls, price ceilings, and price floors. The original intersection of demand and supply numerous proposals have been offered for reducing farm subsidies. A subsidy results in the same price being paid as the market dictates, except for the government pays part of the price. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. Usually set by law, price ceilings are typically applied only to staples such as food and energy products when such goods become unaffordable to regular consumers.